ESOP (Employee stock ownership plan) refers to an employee benefit plan which offers employees an ownership in the organization by issuing Equity shares to them.
ESOPs are issued to select employees in place of immediate monetary compensation. In Post Covid era, many organisations are looking to preserve Liquid Assets for deploying towards business opportunities – thereby increasing focus on ESOPs.
ESOPs encourage employees to do what’s best for shareholders since the employees themselves have their skin in the game as monetization of ESOPs will far exceed the employee’s standard remuneration. ESOPs are in nature of an “OPTION” that could be exercised by employees at a specified Date at specified Price.
Let us with a help of example appraise Rules, Regulations & Terminology associated with ESOPs.
Mr. Aditya joined XYZ Ltd on 1st Jan 2022. He was Granted 10,000 ESOPs on joining to compensate for lower fixed remuneration. As per the grant letter, all the 10,000 ESOPs have a compulsory 24-month cliff period, following which they will vest uniformly over a 4-year period that can be exercised @ Rs.500 / Share.
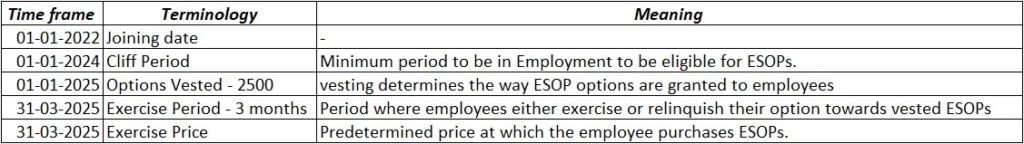
Suppose Aditya exercises his option on 1st Jan 2025 for vested 2,500 shares. He will pay Rs. 12,50,000 as the exercise price (2500 Shares * Rs.500).
Let’s assume the Fair Market Value of share on 1st Jan 2025 is Rs.2000. In this case, he is liable to pay tax on his notional income calculated as (Rs.2000 – Rs. 500) * 2500 Shares = 50 Lacs. It is shown as Perquisite tax.
Once Aditya exercises the option, he is the holder of equity shares that tantamount to purchase of equity shares from the market on that date.
Whenever the shares are liquidated, he is liable to pay Capital Gains tax ( as per the norms).
Period of acquisition would be considered as the date of exercise. Capital Gains tax is like any other equity security, where holding period extending 1 Year gets taxed @10% barring 1 Lac gains and short-term gains are taxed @15% of profit.
To the uninitiated, ESOPs seem to be of complex nature but not really if one understands the simple mechanism as explained above.
Last but most important – Employees must take into consideration risks associated with ESOPs. Concentration Risk (majority of employees asset exposure into one single asset) & Wrong way risk (If company fundamentals deteriorate – employee might lose Job and value of Investments fall).
